Guidance and Counseling Director
g.velasquez2@lajoyaisd.net
School Counseling Department
Contact Information

Gabriela Velasquez

Lisa Garcia
Department Secretary
l.garcia16@lajoyaisd.net
Ph. 956.323.2175

Don Gonzales
Licensed Professional Counselor-Palmview Alignment
d.gonzales@lajoyaisd.net

Juan Guajardo
Licensed Professional Counselor-Juarez Lincoln Alignment
j.guajardo@lajoyaisd.net

Mauro Pena
Licensed Professional Counselor-La Joya Alignment
M.pena10@lajoyaisd.net

Nelson Moya
Behavior Strategist
n.moya@lajoyaisd.net

Jose Rosillo
Behavior Strategist
j.rosillo@lajoyaisd.net

Cynthia Salgado
Behavior Strategist
c.salgado@lajoyaisd.net

How do counselors support the social emotional learning of students?
School counselors serve as a first line of defense in identifying and addressing student social/emotional needs within the school setting. School counselors have unique training in helping students with social/emotional issues that may become barriers to academic success. Within the context of a school counseling program school counselors develop school counseling curriculum, deliver small-group counseling and provide advisement directed at improving students’ social/emotional well-being.
The social/emotional domain is composed of standards to help students manage emotions and learn and apply interpersonal skills as early as preschool and kindergarten (ASCA, 2014). School counselors promote mindsets and behaviors in all grade levels that enhance the learning process and create a culture of college and career readiness for all students in the area of social/emotional development.
According to a meta-analysis by Durlak, Weissberg, Dymnicki, Taylor and Schellinger (2011), students who participated in social/emotional learning programs demonstrated significantly improved social/emotional skills, attitudes, behavior and academic performance that reflected an 11-percentile-point gain in academic achievement when compared with control groups. The American Enterprise Institute and the Brookings Institution (2015) concluded that social/emotional competencies are critically important for the long-term success of all students in today’s economy.
The school counselor is key to identifying students’ social/emotional needs (VanVelsor, 2009). Educational systems as a whole, including school counselors, should graduate students who are not only proficient in core academic subjects but demonstrate an ability to socially and emotionally practice healthy behaviors and behave respectfully when working with others from diverse backgrounds (ASCA, 2007).
School counselors play a role in creating an environment that produces engagement vital to students’ social/emotional development. When students enter high school there is a 40% to 60% chance they will disengage from school (Blum & Libbey, 2004; Klem & Connell, 2004). School performance can be negatively affected when students demonstrate high-risk behaviors such as substance abuse, sex, violence, depression and attempted suicide (Eaton et al., 2008). School counselors address the potential of disengagement by addressing students’ social/emotional development.
The School Counselor’s Role
School counselors play a critical role in supporting social/emotional development as they:
Collaborate with classroom teachers to provide the school counseling curriculum to all students through direct instruction or providing lesson plans for learning activities or units in classroom aimed at social/emotional development (ASCA, 2019).
Understand the nature and range of human characteristics specific to child and adolescent development.
Identify and employ appropriate appraisal methods for individual and group interventions that support K-12 students’ social/emotional development.
Know and utilize counseling theories to inform both direct and indirect services providing support to K-12 students’ social/emotional development.
Select and implement technology in a school counseling program to facilitate K-12 students’ social/emotional development.
Serve as a referral source for students when social/emotional issues become too great to be dealt with solely by the school counselor, including crisis interventions.
In summary, school counselors are committed to supporting students’ social/emotional needs. As advocates for students, school counselors promote a positive environment that enhances students’ ability to properly manage the social/emotional demands of their lives. School counselors use appropriate appraisal methods to promote a school environment designed to propel students toward positive mindsets and behaviors supporting social/emotional development through direct (e.g., classroom curriculum group counseling and individual counseling) and indirect (e.g., collaborating or consulting with staff, families or communities) services.
Source: ASCA
Social Emotional Learning
The La Joya ISD School Counseling Department coordinates the implementation and growth of culturally responsive and emotionally safe learning environments. Through the implementation of Social and Emotional Learning. School counselors provide resources to help students develop skills to manage their emotions, form positive relationships, feel empathy for others, and make responsible decisions. SEL programming is based on the understanding that the best learning emerges in the context of supportive relationships that make learning challenging, engaging, and meaningful.
Social and emotional learning (SEL) is an integral part of education and human development. SEL is the process through which all young people and adults acquire and apply the knowledge, skills, and attitudes to develop healthy identities, manage emotions and achieve personal and collective goals, feel and show empathy for others, establish and maintain supportive relationships, and make responsible and caring decisions.
SEL advances educational equity and excellence through authentic school-family-community partnerships to establish learning environments and experiences that feature trusting and collaborative relationships, rigorous and meaningful curriculum and instruction, and ongoing evaluation. SEL can help address various forms of inequity and empower young people and adults to co-create thriving schools and contribute to safe, healthy, and just communities.
Source: Collaborative for Academic, Social, and Emotional Learning (CASEL)
The CASEL Framework
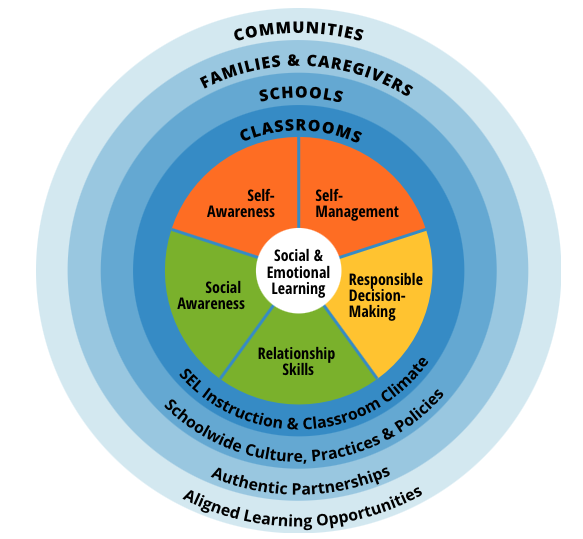
The CASEL 5
Self-Awareness:
The abilities to understand one’s own emotions, thoughts, and values and how they influence behavior across contexts. This includes capacities to recognize one’s strengths and limitations with a well-grounded sense of confidence and purpose.
Such as:
Integrating personal and social identities
Identifying personal, cultural, and linguistic assets
Identifying one’s emotions
Demonstrating honesty and integrity
Linking feelings, values, and thoughts
Examining prejudices and biases
Experiencing self-efficacy
Having a growth mindset
Developing interests and a sense of purpose
Self-management:
The abilities to manage one’s emotions, thoughts, and behaviors effectively in different situations and to achieve goals and aspirations. This includes the capacities to delay gratification, manage stress, and feel motivation and agency to accomplish personal and collective goals.
Such as:
Managing one’s emotions
Identifying and using stress management strategies
Exhibiting self-discipline and self-motivation
Setting personal and collective goals
Using planning and organizational skills
Showing the courage to take initiative
Demonstrating personal and collective agency
Social Awareness:
The abilities to understand the perspectives of and empathize with others, including those from diverse backgrounds, cultures, and contexts. This includes the capacities to feel compassion for others, understand broader historical and social norms for behavior in different settings, and recognize family, school, and community resources and supports.
Such as:
Taking others’ perspectives
Recognizing strengths in others
Demonstrating empathy and compassion
Showing concern for the feelings of others
Understanding and expressing gratitude
Identifying diverse social norms, including unjust ones
Recognizing situational demands and opportunities
Understanding the influences of organizations and systems on behavior
Relationship Skills:
The abilities to establish and maintain healthy and supportive relationships and to effectively navigate settings with diverse individuals and groups. This includes the capacities to communicate clearly, listen actively, cooperate, work collaboratively to problem solve and negotiate conflict constructively, navigate settings with differing social and cultural demands and opportunities, provide leadership, and seek or offer help when needed.
Such as:
Communicating effectively
Developing positive relationships
Demonstrating cultural competency
Practicing teamwork and collaborative problem-solving
Resolving conflicts constructively
Resisting negative social pressure
Showing leadership in groups
Seeking or offering support and help when needed
Standing up for the rights of others
CASEL Video: Relationship Skills
Responsible Decision-Making:
The abilities to make caring and constructive choices about personal behavior and social interactions across diverse situations. This includes the capacities to consider ethical standards and safety concerns, and to evaluate the benefits and consequences of various actions for personal, social, and collective well-being.
Such as:
Demonstrating curiosity and open-mindedness
Learning how to make a reasoned judgment after analyzing information, data, and facts
Identifying solutions for personal and social problems
Anticipating and evaluating the consequences of one’s actions
Recognizing how critical thinking skills are useful both inside and outside of school
Reflecting on one’s role to promote personal, family, and community well-being
Evaluating personal, interpersonal, community, and institutional impacts
CASEL Video: Responsible Decision-Making
Free Resources that offer Mindfulness Practices
Mindful Powers
Mindful Powers™ is a kid-first, holistic approach to building social-emotional learning through the power of play. Built on a skills-based methodology that helps children in early and middle childhood build a healthier relationship with life, stress, and anxiety, Mindful Powers™ empowers kids to bring calm to their lives at the touch of their fingertips.
Provides Individualized Practices
Smiling Mind
Smiling Mind has been at the forefront of mental wellbeing innovation for over 12 years, helping minds thrive with evidence-based tools and resources. Their mission is Lifelong Mental Fitness. Smiling Mind aims to create generational change in mental health, providing proactive tools and programs that help every mind thrive. They have impacted millions of people through their renowned mental wellbeing app and school based programs—but this is just the beginning.
Appropriate for all Levels
3 categories to Explore (Classroom, Parents, Workplace)
Each category has levels
Each level has 20 practice sessions
Virtual Calming Room
This Virtual Calming Room is a place for students, families and staff to find tools and strategies for managing emotions and feelings.
Free Career Interest Inventory Resources
Hello La Joya ISD, the counseling department would like to provide you with the tools to help you identify career interests and help you get ready for college. It's never too early to prepare for the future and our job is to help you through your journey. What interests intrigue you? What captivates you so much that you would want to spend the rest of your life doing this special interest? Career interest inventories are testing instruments designed to help students learn more about themselves, as well as identify careers that would be a good fit based on their interests. The results of the assessments guide students in discovering more about themselves, as well as occupations that are the best fit for them. Inventories help students understand their career possibilities so they can make well-informed decisions about their future. Career inventories are a “bridge that brings concepts into exploration.
Career inventories provide vital information needed for the career planning process, and they aid students in eliminating career choices that are not the best fit. Career inventories allow students to explore further career pathways based on interests, values, and skill sets.
Interest Inventory Resources
· College Board Interest Inventory
· Elementary Interest Inventory
· EVERFI
· Holland Code Test (6th Grade)
· ICAN

Going Beyond College and Career Readiness
Traditionally, college and career readiness (CCR) in schools has been focused around three areas: academic skills, career knowledge, and college knowledge.
With this laser focus, students understand the importance of succeeding in classes and preparing for standardized tests, as well as various aspects of careers. Students also prepare for college by conducting college and scholarship searches, determining their college major, and ultimately applying to college. For some students, this is enough. However, in today’s world of work, hard skills only take a student so far. Social and Emotional Learning (SEL) and essential life skills are crucial to future success, especially when considering equity and the 33% of first-generation students who graduate from high school every year.
With that in mind, it’s time to expand the definition of college and career readiness. Although academic, career and college knowledge are vital to a student’s future success, they also need to be equipped with the skills to succeed after high school—whatever path they may choose. When students understand their strengths, know how to overcome obstacles, and learn how to set goals effectively, they can carry those skills through to all areas of their life. When they learn successful teamwork skills and know their online presence, they become an effective employee. Moreover, when they understand how to make successful transitions, they are equipped for life.
Source: WHITEPAPER: Expanding the Definition of College and Career Readiness - The CCLR Framework
The College Career and Life Readiness (CCLR) Framework provides a blueprint to prepare middle and high school students for success after graduation. This practical tool set helps our schools define, measure, and track success for our college, career and life readiness initiatives.
As part of the CCLR Framework, there are lessons that counselors and teachers can use to develop students’ social emotional skills. Competencies and themes include:
Social Emotional Learning
Strengths
Interests
Emotional Intelligence
Grit
Self-Awareness
Informed Decisions
Transition Skills
School Transitions
Preparing for College
Preparing for Life
Postsecondary Goal Setting
Teamwork
Interpersonal skills
Support Network
Getting Involved
Communication Skills
Online Presence
Why do these themes matter?
Students who understand their strengths can begin to build goals toward a future that best fits their interests and skills. When students develop grit and perseverance, they are better able to overcome obstacles they are faced with in school and life.
Teamwork, communication and digital literacy development are important to produce students who are able to advocate for themselves and be productive in the workplace. Students who identify and rely on their support systems have positive postsecondary outcomes.
Transitions are a part of life as a student, from elementary school through career placement. Building coping skills around transitions from elementary to middle school to high school, then to independent life can help students to successfully adapt to new situations.
Source: The College, Career and Life Readiness Framework (Naviance by Power School)
Youth Mental Health First Aid
What is Mental Health?
“Mental health includes our emotional, psychological, and social well-being. It affects how we think, feel, and act. It also helps determine how we handle stress, relate to others, and make choices. Mental health is important at every stage of life, from childhood and adolescence through adulthood. (MentalHealth.Gov)
Are youth impacted by Mental Health Challenges and Disorders?
10.2% of youth will be diagnosed with a substance use disorder in their lifetime. (Source: Youth Mental Health First Aid)
1 in 5 teens and young adults lives with a mental health condition. (Source: National Alliance for Mental Illness)
50% of all mental illnesses begin by age 14, and 75% by the mid-20s. (Source: Archives of General Psychiatry)
La Joya ISD (Addressing Student Mental Health Needs)
La Joya ISD prioritizes mental health. Mental health challenges and disorders are real, and have a powerful impact on student academic and social & emotional success. As such, La Joya ISD utilizes the Youth Mental Health First Aid Program from National Council for Mental Wellbeing as a tool in ensuring that the mental health needs of students are met appropriately and efficiently.
La Joya ISD makes this training available to all district staff. District Behavior Specialists with the LJISD School Counseling Program currently hold national certifications to train Youth Mental Health First Aid. Training dates are scheduled by the School Counseling Department. La Joya ISD staff are thus able to become certified in Youth Mental Health First Aid within La Joya Independent School District.
Why Youth Mental Health First Aid?
Youth Mental Health First Aid teaches you how to identify, understand and respond to signs of mental health and substance use challenges among children and adolescents ages 12-18.
What does Mental Health First Aid cover?
Mental Health First Aid covers common signs and symptoms of mental health challenges in this age group, including anxiety, depression, eating disorders and attention deficit hyperactive disorder (ADHD).
Mental Health First Aid covers common signs and symptoms of substance use challenges.
Mental Health First Aid covers how to interact with a child or adolescent in crisis.
Mental Health First Aid covers how to connect the youth with help.
Mental Health First Aid covers expanded content on trauma, substance use, self-care and the impact of social media bullying.
How is this training relevant to educators?
Educators work with students on a daily basis. Thus, they have the valuable opportunity to interact with students frequently. During interactions, educators are able to observe/notice any changes in behavior, and identify immediate needs that may be evident. Youth Mental Health First Aid provides educators with additional tools to ensure that student mental health needs are met successfully.
What is the Mental Health First Aid Action Plan?
Assess for risk of suicide or harm.
Listen nonjudgmentally.
Give reassurance and information.
Encourage appropriate professional help.
Encourage self-help and other support strategies.
Trauma Informed Care Training (Professional Development Topic)
La Joya ISD prioritizes Mental Health and Social & Emotional Learning. Unfortunately, children at times become victims to life circumstances, and experience trauma. It is critical that we as educators are able to recognize trauma in children, and provide immediate support when needed. La Joya ISD School Counselors provide annual training to all district staff on Trauma Informed Care.
Why is Trauma Informed Care relevant?
As adults, we must create a paradigm shift from the question: “What is wrong with you?” to “What have you experienced?” and “How can I assist you?”
Ask yourself:
Is what I am doing respectful and trauma-informed?
Am I treating others the way I want to be treated?
Traumatic Events are:
Sudden, unexpected, and extreme
Usually involve physical harm or perceived life threat (research shows the perception of “life threats” are powerful predictors of the impact of trauma)
People experience these events as out of their control
Certain stages of life makes people vulnerable to the effects of trauma including childhood, teens and early twenties.
What is Child Traumatic Stress?
Child traumatic stress is the physical and emotional response a child has to events that pose a threat to the child or someone important to them.
When a child experiences trauma, the child may be unable to cope, have feelings of terror and powerlessness and experience physiological arousal they cannot control.
A traumatic event can affect the way children view self, the world around them, and their future.
Long-Term Effects of Childhood Trauma
When a traumatized child does not cope with trauma in a healthy manner, the child may be prone to:
Substance abuse
Mental health issues (such as depression and suicide)
Difficulty forming and maintaining positive relationships with friends and adults
Promiscuity
Criminal behavior
What You Can Do
Forming trusting attachments and relationships is critical for children who have suffered trauma.
There are several things you can do to help establish a trusting relationship with a child, such as:
Have quality interactions with the child (this means fully engaging with the child and listening to the child)
Do not make commitments or promises that you may not be able to keep
Involve the child in decisions that affect their lives
Focus on the child’s strengths and resilience
Refer to the school counselor and outside agencies for support
Surround the student with positive role models and mentors
Additional tips for working with traumatized children:
Set up relationships and situations that avoid re-traumatizing children.
Work with children to discover their "triggers" and ways to stay safe
Focus on children's strengths; what they CAN do, assist with coping skills
Understand that a child’s behavior is likely the result of coping mechanisms and survival techniques.
Teacher Resources
What teachers should know about SEL?
At La Joya ISD we encourage our educators to practice SEL not only for their students but also for their own personal benefits. Social-emotional skills not only improve academic outcomes and classroom behavior for students, they can also have a positive impact on our own personal and professional success as educators. To teach SEL, we need to be aware of and continue to develop our own social-emotional skills. Only then can we model and teach those skills to our students.
As a starting point, both educators and students need to feel valued and safe. The Collaborative for Academic, Social, and Emotional Learning (CASEL) developed a framework that defines five core competencies of SEL. In this section we will share strategies on the 5 SEL competencies.
Teacher Strategies (for Classroom Use)
The following strategies can be used by educators to teach students how to self-regulate their emotions.
Mood Meter Handout
The Mood Meter is a tool we use to recognize and understand our own and other peoples’ emotions. Here’s how it works.
The Mood Meter is divided into four color quadrants – red, blue, green, and yellow – each representing a different set of feelings. Different feelings are grouped together on the Mood Meter based on their pleasantness and energy level.
RED feelings: high in energy and more unpleasant (e.g., angry, scared, and anxious);
BLUE feelings: low in energy and more unpleasant (e.g., sad, disappointed, and lonely);
GREEN feelings: low in energy and more pleasant (e.g., calm, tranquil, and relaxed);
YELLOW feelings: high in energy and more pleasant (e.g., happy, excited, and curious).
Once we become more aware of our emotions, we begin to notice how they impact our decisions and behaviors. As we use the mood meter, we will begin to recognize which quadrant of the Mood Meter we’re in, have the ability to name the precise emotion we are experiencing (elation, dismay, anxiety, calmness, curiosity…), and develop strategies for working with a range of emotions.
When children have the vocabulary to describe what’s going on in their inner life, they are going to have a better idea about what to do next, in their outer life. The Mood Meter is a tool that helps us build our skills of emotional intelligence
SAMPLE SCRIPTS to help students label emotions on the Mood Meter
Where are you on the MOOD METER?
What is causing you to feel this way?
What word best describes your feeling?
How are you expressing this feeling?
Are you comfortable expressing?
How do you want to feel? What strategy will you use to stay or shift?
Script to use with the MOOD METER When a Student is NOT in a Positive Quadrant
Right NOW, I feel: __________________
Feeling this way is helpful to what I’m doing? YES / NO
If the answer is no, answer this: I would like to feel ______________ instead.
To get to the desired emotion, I can insert strategy here.
(use the regulation strategies from the mood meter)
2. Utilize thinking strategies
Strategy: | How it Works: |
|---|---|
Self-Talk | When you notice you have catastrophic thoughts, change the narrative by giving yourself a pep-talk. |
Distancing | See yourself as an observer in an intense situation you are a part of. |
Reframing | Look to see different perspectives other than your own. |
Distraction | When you find yourself ruminating, disrupt the signal by doing something different for a short period of time.
|
Labeling | Keep a log of the emotions you experience. Naming what you feel is the gateway to reducing the intensity of high energy, unpleasant emotions. |
Action Strategies
Strategy: | Builds Positive Energy: | Reduces Unpleasant Emotions: | Calming and Restorative: |
|---|---|---|---|
Take a conscious Breath |
| ● | ● |
Stretch in your chair |
|
| ● |
Listen to music | ● | ● | ● |
Make yourself a hot cup of tea |
|
| ● |
Sit with your pet | ● | ● | ● |
Go for a walk | ● | ● | ● |
Exercise | ● | ● |
|
Call a friend | ● | ● | ● |
Engage in a hobby | ● | ● | ● |
Take a nap |
|
| ● |
Keep a journal |
|
| ● |
Help a person in need | ● | ● | ● |
Dance in your living room | ● | ● |
|
Watch something that makes you laugh | ● | ● |
|
Stand outside for 2 minutes |
|
| ● |
Parent Resources
This page has helpful resources and topics that are geared toward helping families and children. If you have questions about any of these resources, please see your school counselor. There are many great websites available for parents. Just click on the link below each question to find out ways that you can help your child learn and grow!
How can I help my child calm down?






